England Voltage Guide: What You Need To Know
Are you planning a trip abroad, and concerned about whether your electronics will function? Understanding the electrical landscape of your destination is crucial for a smooth and safe travel experience, and the voltage is a key factor to consider.
When venturing to different countries, it is essential to be aware of the voltage, frequency, and plug type used in that region. Just as the rest of Europe, the United Kingdom operates on a standard voltage of 230 volts at a frequency of 50 Hz. This information is crucial for ensuring the compatibility of your electrical devices and preventing any potential damage.
The electrical systems across the globe present a diverse landscape, and navigating this can often be confusing. Fortunately, standardized voltage levels and plug types help to streamline the process, making it easier for travelers to adapt and remain connected.
The UK, like many countries, utilizes a mains supply that falls within a specific voltage range. In the United Kingdom, this is 230 volts, while the frequency, which measures cycles per second, is 50 Hz. This frequency is identical across the majority of European nations. Devices with ratings between 220 and 240 volts can safely be used, which is something to consider before packing your bags.
When considering the use of electrical appliances, a three-pin adapter is often required. The power sockets in England use Type G plugs, which have three rectangular pins. This plug type is characteristic of the UK and Ireland and therefore, if your devices have a different plug configuration, you will need an adapter.
Some electronic devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are often dual voltage. This means they can handle both 110V and 220V, making them compatible with a wider range of power outlets. However, it's essential to check the specifications of your device to confirm its voltage compatibility before plugging it in.
The United States, for example, utilizes a lower voltage standard (120V) than the UK, at 230V. This substantial difference requires careful consideration, and the use of a voltage converter might be necessary for devices not designed for the UKs voltage. If your device is rated at 120V, using it directly in the UK without a converter could cause damage.
If your electronic items are not dual voltage, a voltage converter might be necessary to ensure safe and correct operation. A voltage converter transforms the UK's 230V supply into the 120V needed by US-based devices. Keep in mind that you may need both a voltage converter and a plug adapter. It is important to consider the power consumption of your devices when selecting a voltage converter.
For many devices, the standard voltage in the UK is 230V. Devices rated between 220 and 240V can be used safely without a voltage converter. However, it's always a good idea to check the voltage label on the appliance before connecting it.
Remember that the electricity from a wall socket is Alternating Current (AC) voltage, which changes polarity over time. The frequency of this change is measured in Hertz (Hz). In the UK and most of Europe, this frequency is 50 Hz. In contrast, the US uses 60 Hz.
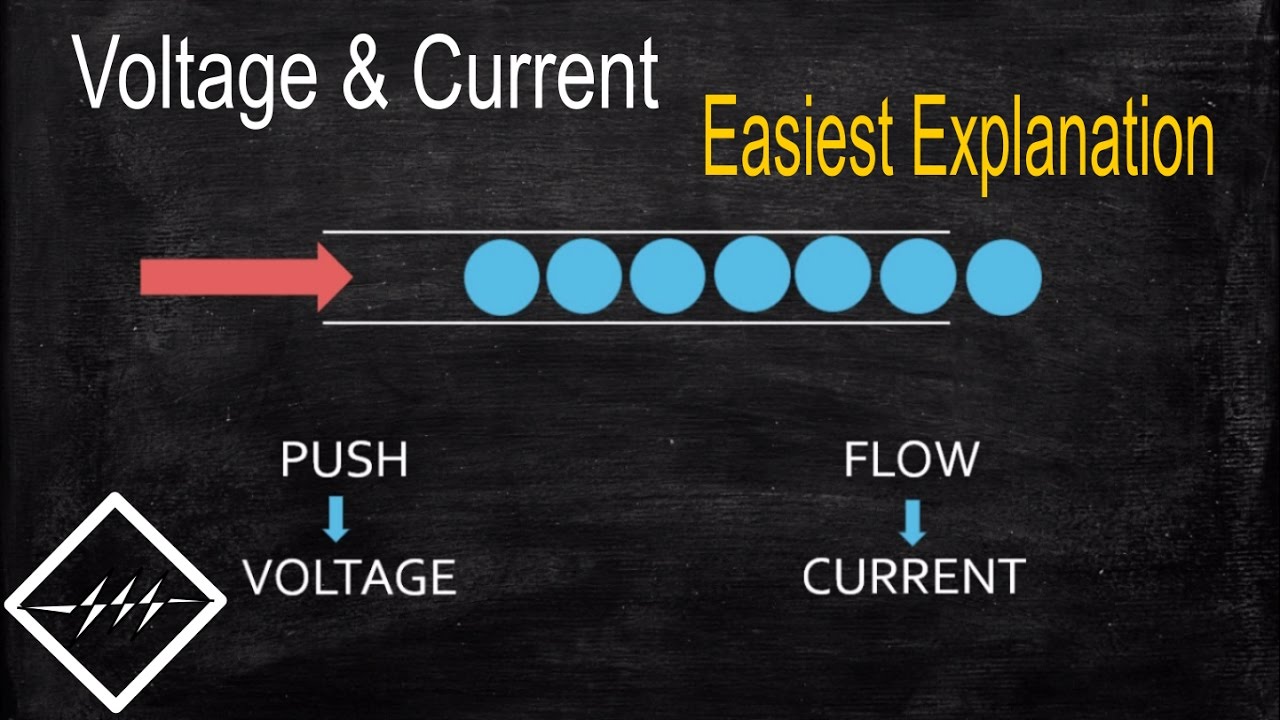
Voltage is fundamentally the force that drives the flow of electric current, measured in volts. It represents the potential energy difference per unit charge between two points in an electrical field. You can think of voltage like water pressure in a hydraulic system, with higher pressure (voltage) driving electrons through a circuit.
There is more to consider than just voltage. The quality of the electrical supply is also important. While the UK grid provides a stable supply, fluctuations can occur. These can be small, brief changes, or larger disturbances. For instance, average root mean square (RMS) values of voltage, which help measure the effective value of a varying voltage waveform, are typically stable. However, there can be variations.
Voltage changes and flickers, which are rapid fluctuations in voltage, might occur infrequently. These can affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices. The power quality of the electricity grid can also affect any sensitive electronic devices. These include power dips, which are sudden reductions in voltage. These dips are usually short-lived, but can cause issues with certain equipment.
When preparing for a trip to the UK, remember to verify your devices' voltage compatibility. The correct voltage can prevent damage. If you need a voltage converter, choose one appropriate for the power consumption of your devices. The choice of voltage converter depends on your needs.
For more technical insights into electrical systems and power quality, you may find resources on official websites like the relevant standards bodies or electrical engineering associations.
In essence, when you consider the type of adapter you'll need in the UK, a three-pin adapter is often the solution, assuming your devices are compatible with 230V. The UK has a standard voltage of 230V at 50Hz.
The standard voltage in England is 230V, with a frequency of 50Hz. The power sockets utilize Type G plugs. The appliance can be plugged into outlets ranging from 220V to 240V without a voltage transformer, but a socket adapter is often required if the plug doesnt match. While a voltage converter is often not necessary for appliances rated between 220-240V, a travel adapter is often vital.
Whether you're a seasoned traveler or planning your first international trip, understanding these basics will ensure a more secure and enjoyable travel experience. Being informed about the voltage and plug types in your destination will prevent any unfortunate surprises and allow you to keep your essential devices powered.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Standard Voltage | 230V |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Plug Type | Type G (three-pin) |
| Dual Voltage Devices | Many devices such as laptops and smartphones are dual voltage and can handle both 110V and 220V |
| Voltage Converter Required | Often not required for devices rated 220-240V, but required for devices rated 110-120V |
| Travel Adapter Required | Often required to convert the plug type |
| AC Voltage | Alternating Current, the type of electricity from the wall socket |
| Frequency in America | 60 Hz |
| Power Dips | Short reductions in voltage that might occur. |
| RMS values | Measure of effective voltage of a varying waveform. |
For further information, consult travel guides, or visit official electrical standards websites.